
Privacy (Australian Privacy Act 1988)
There are legal requirements for large companies and companies who hold sensitive information (medical businesses, gyms, market research, schools, etc) about the public to protect that […]

There are legal requirements for large companies and companies who hold sensitive information (medical businesses, gyms, market research, schools, etc) about the public to protect that […]

Data normalisation organises data in a database (across multiple tables/entities/relations) to ensure there is no data redundancy and to avoid anomalies (insert, deletion, update). There […]

Full backup is a backup of all the data, this is the initial backup. Incremental backup backs up data that has been modified since the […]

The code below is Pseudocode. Sequence Sequence is each statement after another. x = 0 OUTPUT (“Hello world”) are examples. Selection When a decision needs […]

Protocols are agreed forms of communication. Computer networks require protocols to transfer different types of data reliably and efficiently – and sometimes securely – most protocols […]

Topology is the arrangement of network devices and their connection. The star topology is most commonly used as it is the most fault tolerant. If […]

Transmission media (or medium) refers to any method of network connection, whether it is wired or wireless. They all transfer packets of data using different […]
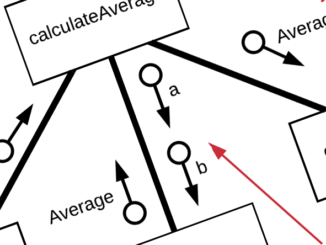
Structure charts show the functions/modules within software and the parameters passed between them. Note: the only symbols you need to use are process and data […]

Recap of both the videos above:

Data integrity is about ensuring all data is consistent and accurate throughout a database. Referential integrity ensures all foreign keys have a primary key in another […]
Copyright © 2025 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes