
Digital signatures are very much like handwritten signatures, they are proof of authenticity. Digital signatures are one of the three data protection methods of authentication.
A message (e.g. email message, document) is passed through an algorithm that uses the senders private key (see encryption) to generate an encrypted hash. The hash is attached to the original document and sent to the receiver (the method of sending may also use encryption, but that is separate to digital signatures). The receiver uses the senders public key to decrypt the hash and compare it to the message’s hash to test if the message is authentic.
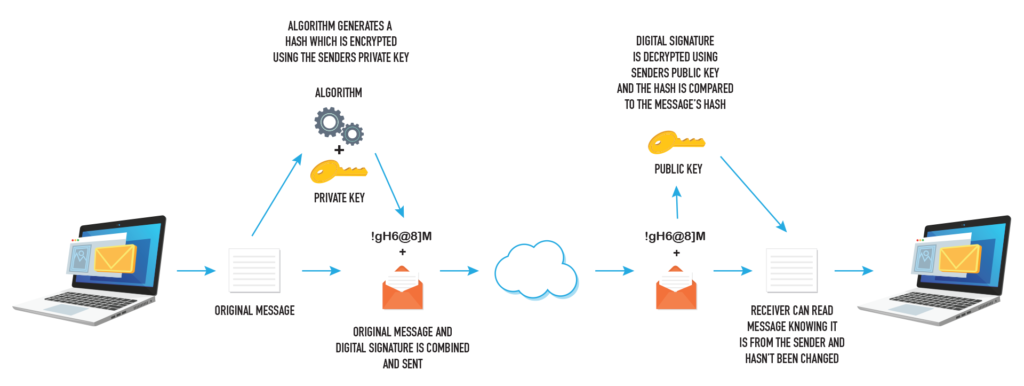
Authentication
Digital signatures ensure messages are really from the sender. This requires the senders private key to
Integrity
Digital signatures ensure the message sent has not been changed after being sent. If any changes occur after the hash has been generated the resulting decoded hash will not match the senders hash.
Non-repudiation
A digital signature proves a message had to have come from a particular sender; they cannot deny